Behind the Numbers: Who Is Killing Their Own Team?
Posted by KCarpenter on December 1st, 2011A lot of the effort in basketball analytics goes towards the good things that players do that do not appear in the box score. This is the driving idea behind Michael Lewis’s seminal New York Times feature, “The No-Stats All-Star,” an early look at analytics in the NBA primarily focused on Darryl Morey, Shane Battier, the Houston Rockets, and adjusted plus/minus. This makes sense: finding hidden strengths is the coach’s angle while finding hidden value is the economist’s angle. As a result of the fine work of smart guys with formulas and others with a willingness to watch a lot of games closely, Charles Jenkins and Nate Wolters were household names last season. This, of course, assumes that your household is filled with basketball dorks, but you get the idea.
Finding diamonds in the rough is a noble pursuit and talking up the greatness of underexposed and underrated players is a worthwhile task (Hey there, Kenneth Faried!). Sometimes, however, there is a joy in using analytics and “advanced” statistics to look for the guy who is hurting his team the most. Let’s ignore the diamonds and go straight for the rough.
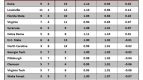
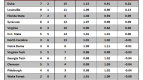
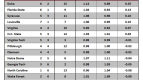
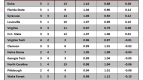
How does a player hurt his team? Well, when push comes to shove, there are basically only two ways: offensively and defensively. Sadly, however, contemporary box scores assign no grade for bad defense to the individual outside of counting how many fouls (which could very well be offensive) a player commits. Our primary understanding of player’s individual defense comes only in positive contributions like blocks, steals, and defensive rebounds while the effect on an opponents shooting percentage is measured at a team level. The noble effort of Luke Winn, David Hess, and others that has sought to enact Dean Oliver’s defensive charting schemes is a good start at really quantifying individual defense, but a very small percentage of Division I games have been looked at in this way making the approach of limited use to someone who wants to look at the whole of college basketball. So, acknowledging that analytic approaches to finding bad defensive players are limited, let’s at least take a quick look at fouls.