Overvaluing Previous Year’s Success in Preseason Rankings
Posted by William Ezekowitz on November 20th, 2015Part of what makes college basketball both exciting and maddening is that each year we have to throw out the previous year’s assumptions and start from scratch. If that wasn’t apparent before this season started, it became painfully obvious when mighty Wisconsin, last year’s national runner-up, lost to Western Illinois, the worst team in last year’s Summit Conference. But perhaps it is the case that we don’t erase the previous year from our memory at the beginning of each season as much as we should. The Badgers, despite retaining just three of the eight players who earned meaningful minutes and bringing in zero top 100 recruits, were still ranked 17th in the preseason polls. In fact, 13 of last year’s Sweet Sixteen teams started the season in the USA Today Preseason Top 25. Can the success of all of these programs be so stable? Or are we perhaps suffering from recency bias, where we tend to overvalue teams that have recently succeeded, even if the personnel structures of those teams have drastically changed?
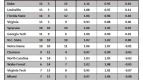
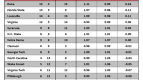
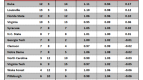
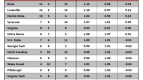
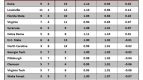
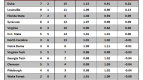
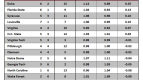
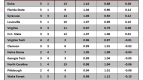
In order to answer this question, I checked the preseason and postseason USA Today Coaches’ Polls (with postseason being taken after the conclusion of the NCAA Tournament), and checked how many Sweet Sixteen teams from the previous season were in each poll. If we are overvaluing Sweet Sixteen teams, then there would consistently be more teams from the previous year’s Sweet Sixteen in the preseason poll than in the postseason poll, which would indicate that Sweet Sixteen teams have dropped out due to poor performance.
This is exactly what has happened. Going back seven years, the number of previous year’s Sweet Sixteen teams has always been greater in the preseason poll than in the postseason poll. Of 112 possible Sweet Sixteen teams to choose from in those seven years, 77 have appeared in the preseason poll and just 61 have appeared in the postseason poll. A difference of proportions test reveals that these two numbers are significantly different from each other at the 95 percent confidence level, which, in layman’s terms, means that this trend is too strong to write off as pure coincidence.