Behind the Numbers: VCU & Butler Prove the Limits of Analytics
Posted by KCarpenter on April 7th, 2011Continuing on: there is not a single analytic, logical or evidence-based approach that would have predicted VCU in the Final Four. Let’s be perfectly clear about this. In basketball analytics, most systems aim to predict likely future performance based on past performance and from that data calculate the most likely outcome. VCU in the Final Four was not a likely outcome by anyone’s reckoning. Sure, a few brackets had VCU in the Final Four, but that wasn’t because of rigorous analysis of match-ups or quantum wavelength formulas that are beyond us. Anyone who put VCU in the Final Four knew that it was an unlikely outcome. Maybe they put the Rams in because they were alums. Maybe their aunt lives in Richmond. Maybe they just think Shaka Smart is a handsome man (he is!). Maybe they picked the Rams because they knew few people would. All of these people who did actually pick VCU knew that it was a longshot as opposed to something that would probably happen.
This is smart. This is how you make brackets. Remember this. When there are thousands of different possible permutations, the most likely outcome is still pretty unlikely. An all-chalk bracket seems much more likely than any number of brackets in recent years, but it has still never happened. Hell, we’ve only had one year of all four number one seeds making the Final Four. On a gut level do you feel that there is a significant difference between 1,000,000-to-1 odds and 1,500,000-1 odds? At the level of the infinitesimally unlikely, even big differences don’t seem to matter that much. I say this not as anti-mathematical nihilism, but to bring a sense of perspective to unlikely events. So here’s what I’m saying: when the most likely outcome is still incredibly unlikely to turn up, how surprising is it when something extremely unlikely happens? There is a real math answer if we gave these outcomes values, but the important answer, the one that we feel in our gut is that, no, it’s not really any more surprising than the other infinite variations of weirdness that the tournament spits at us every March.
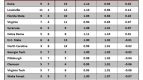
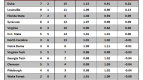
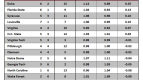
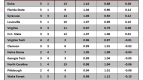
Every bracket is a longshot prediction at a perfect bracket, which is such a rare and magnificent beast that not a single one was spotted this year (or any year, for that matter). In the ESPN bracket challenge, only two submissions out of 9.5 million even got the Final Four right. Long odds to get the bracket right, but of course, the odds that the teams themselves faced were not insignificant. Far smarter minds than mine have looked at the unlikeliness of the overall composition of this Final Four, the incredible journey of VCU to the Final Four, and the surprise of Butler in two back-to-back Championship Games; and while the supposed rarity and oddity of each of these accomplishments is interesting, it’s important not to lose sight of the big picture question: How did all these supposedly unlikely things happen and no one see any of them coming?