UAB Fines Athletes to Improve Academic Standards; Slippery Slope?
Posted by Chris Johnson on August 21st, 2012Christopher Johnson is an RTC columnist. He can be reached @ChrisDJohnsonn.
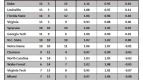
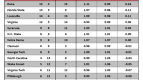
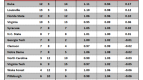
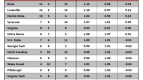
Earlier this year, Connecticut was one of 10 college basketball teams to receive a one-year postseason ban for not meeting the NCAA’s minimum four-year Academic Progress Rate (APR) threshold of 900. The Huskies filed an appeal, arguing that recent reforms had produced increased scores over the past two years. In the end, though, the NCAA stuck to its guns and reaffirmed its initial ruling. And so it was that UConn – a program that has experienced a rapid rise into the college hoops elite under coach Jim Calhoun – just one and a half years removed from winning a national championship, was banned from the sport’s pre-eminent postseason tournament. The Huskies probably won’t feel any measurable downturn in recruiting success or national cachet as a result, but the sentencing proved that even the sport’s marquee brands are vulnerable to the NCAA’s increased academic standards.

After struggling to keep up with the NCAA’s APR standards, UAB is going new lengths to improve its academic standing in the coming years.
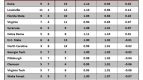
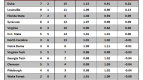
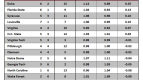
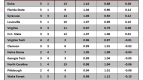
A one-year postseason ban in men’s basketball doesn’t come close to the sort of multi-faceted, crippling atom bomb the NCAA dropped on Penn State. Alabama-Birmingham is nonetheless determined to avoid a UConn-esque fate, and it’s adopting a unique approach to work toward that end. The program has endured a rough history of keeping up with the NCAA’s academic reforms. During the last measured four-year APR period (2003-07), UAB had six teams fail to meet the minimum mark and was the second-most penalized program in the nation for its academic shortcomings. With that spotty track record, it comes as no surprise that the Blazers are seeking new ways to enforce academic responsibility. In a formal Q & A with the Birmingham News, athletic director Brian Mackin outlined his plan to keep UAB’s various teams above the APR cutline. Along with increased academic support, study time and access to student-athlete advisors, UAB has laced its academic compliance code with monetary disincentives.